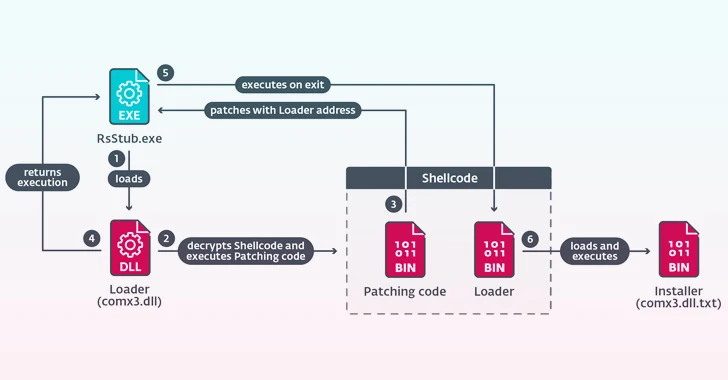
A new China-aligned threat actor named Blackwood has been identified, deploying a sophisticated implant named NSPX30 via the update mechanisms of legitimate software to target Chinese and Japanese companies and individuals.
An external threat actor in possession of a Google account could misuse this misconfiguration by using their own Google OAuth 2.0 bearer token to seize control of the cluster for follow-on exploitation.
The company has discovered a limited number of individuals whose personal information may have been impacted during the breach and is working with a third-party forensics firm to assess the extent of the attack’s impact on its operations and systems.
KB5034204 also fixes an issue caused by a deadlock that prevents search from working on the Start menu for some users and addresses a bug affecting the OpenType font driver, affecting how text renders for third-party applications.
It appears that the package author was in the process of building out the malware and adding layers of deception. Fortunately, the package was detected and removed from npm before that could happen.
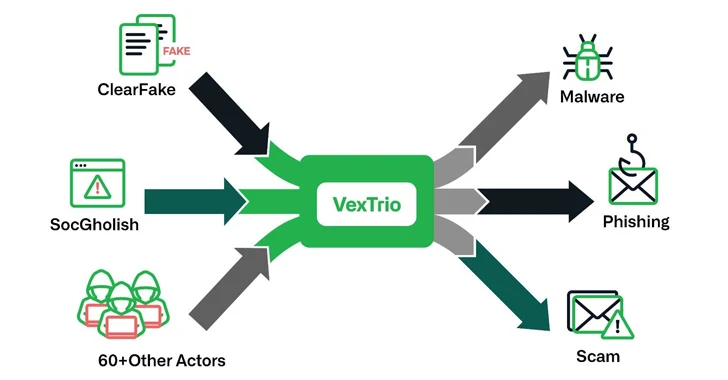
VexTrio has been attributed to malicious campaigns that use domains generated by a dictionary domain generation algorithm (DDGA) to propagate scams, riskware, spyware, adware, potentially unwanted programs (PUPs), and pornographic content.
While most organizations consider cyber resiliency a foundational aspect of their broader business continuity or disaster recovery (BC/DR) strategy, BC/DR preparedness is not yet “passing” most service-level agreement (SLA) expectations.
Deserialization of untrusted data can allow malicious code to be executed on the system. This is because the serialized data can contain instructions that the application will execute when it deserializes the data.
“We do not know the number of accounts that the unauthorized party was able to access, but out of an abundance of caution, we are sending this notice to all potentially affected account holders,” reads the data breach notification from Jason’s Deli.
The ransomware uses targeted phishing techniques for initial access, as well as to gather credentials from one of the employees of its target company. It then uses RATs to gain privileged access and move laterally within its target network.