“Campaigns using versioning commonly target users’ credentials, data, and finances,” Google Cybersecurity Action Team (GCAT) said in its August 2023 Threat Horizons Report shared with The Hacker News.
The database, hosted on Oracle’s cloud and more than 1.7 terabytes in size at the time it was exposed, contained customer’s personal information, including names, gender, dates of birth, home addresses, flight information and passport numbers.
The personal information compromised in the attack includes any combination of the following: name, U.S. Social Security Number, date of birth, home mailing address, Serco and/or personal e-mail address, and selected health benefits for the year.
The National Science Foundation’s NOIRLab did not respond to requests for comment but published a notice on Tuesday night explaining that the lab had discovered an attempted cyberattack on its systems that morning.
A rather sophisticated version of the Rilide malware was identified targeting Chromium-based web browsers to steal sensitive data and cryptocurrency. Experts identified over 1,300 phishing websites distributing the new version of Rilide Stealer along with other harmful malware such as Bumblebee, IcedID, and Phorpiex. Organizations need to leverage the IOCs to understand the nature and attack scope […]
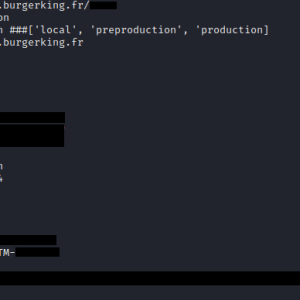
On June 1st, 2023, the Cybernews research team discovered a publicly accessible environment file (.env) belonging to Burger King’s French website, containing various credentials. The file was hosted on the subdomain used for posting job offers.
The list of LOLBAS files – legitimate binaries and scripts present in Windows that can be abused for malicious purposes, will soon include the main executables for Microsoft’s Outlook email client and Access database management system.
The cipher, designed by Assistant Professor Rei Ueno from the Research Institute of Electrical Communication at Tohoku University, addresses the threat of cache side-channel attacks, offering enhanced security and exceptional performance.
Rilide was first documented by the cybersecurity company in April 2023, uncovering two different attack chains that made use of Ekipa RAT and Aurora Stealer to deploy rogue browser extensions capable of data and crypto theft.
The five key risk areas are misconfigurations, external-facing vulnerabilities, weaponized vulnerabilities, malware inside a cloud environment, and remediation lag (that is, delays in patching).