Netscout researchers have identified more than 14,000 existing servers that can be abused by ‘the general attack population’ to flood organizations’ networks with traffic.
Although the US and the United Nations have levied sanctions meant to prevent the illegal financing of nuclear weapons, North Korea is proving to be adept at sidestepping them — and is also remarkably proficient at cybercrime.
The hackers behind the ransomware attack on the Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) have published thousands of stolen files after the organisation refused to pay the ransom.
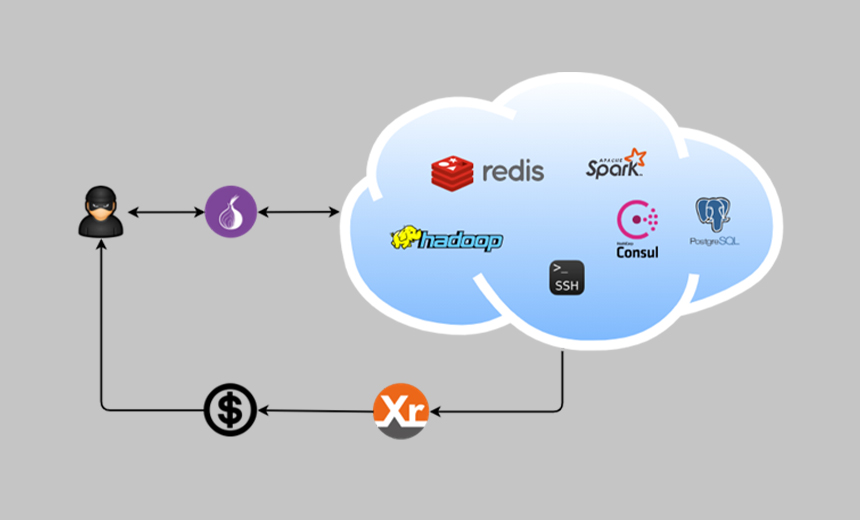
DreamBus presents a serious threat because of the many components it uses to spread via the internet and the wormlike behavior that enables it to move laterally once inside a targeted system, ThreatLabz says.
A home security technician admitted that he secretly accessed the cameras of more than 200 customers, particularly attractive women, to spy on while they undressed, slept, or had sex.
The CursedGrabber malware has infiltrated the open-source software code repository. Three malicious software packages have been published to npm, a code repository for JavaScript developers to share and reuse code blocks.
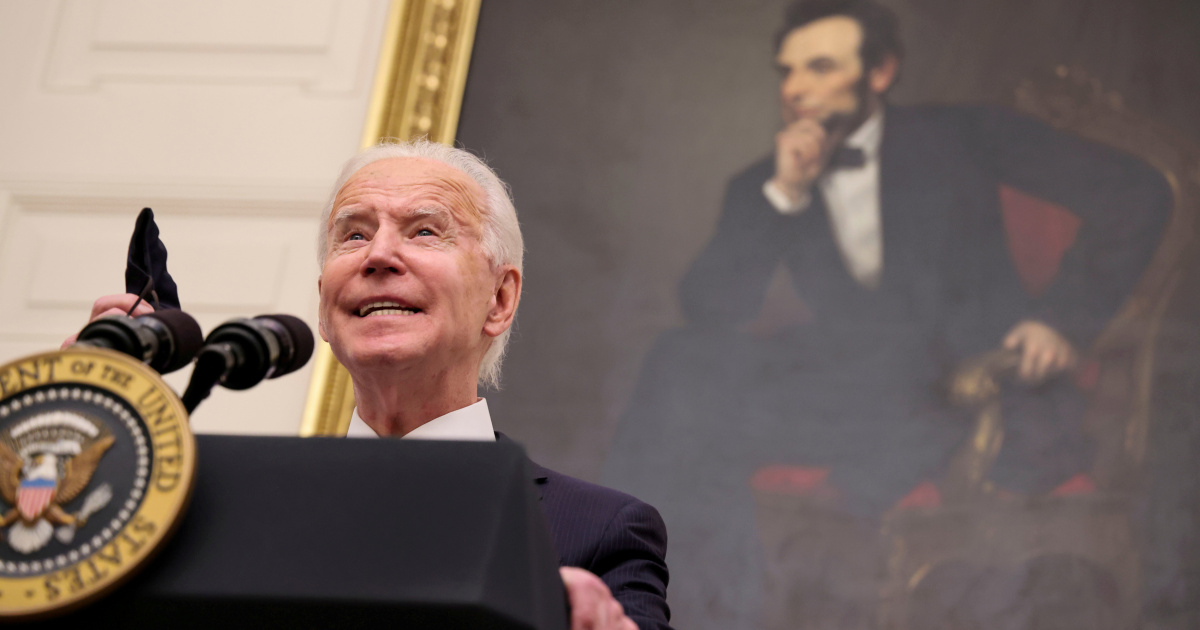
President Joe Biden is hiring a group of national security veterans with deep cyber expertise, drawing praise from former defense officials and investigators as the US government works to recover from one of the biggest hacks of its agencies..
Bonobos clothing store has suffered a massive data breach exposing millions of customers’ personal information after a cloud backup of their database was downloaded by a threat actor.
To protect useful attack vectors through SolarWinds, Microsoft, and VMWare, the hackers made every effort not to reuse infrastructures or settings or to tie one stage of the attack to another.
The Russian government has issued a security alert warning Russian businesses of potential cyberattacks launched by the United States in response to the SolarWinds incident.