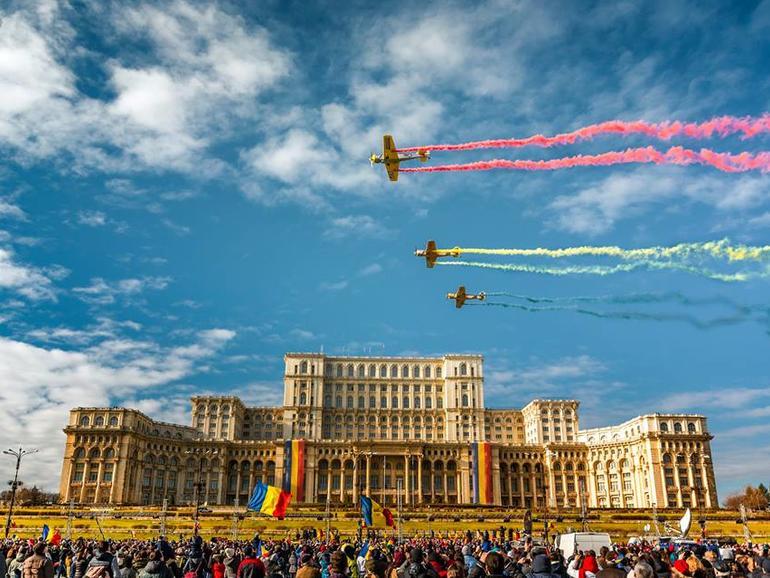
The European Council voted to locate the EU’s future cybersecurity research hub in Bucharest, Romania’s capital. Named the European Cybersecurity Industrial, Technology and Research Competence Centre,, the new hub is set to start operating next year.
A potential remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability has been patched in one of Starbucks’ mobile domains. A CVE has not been issued for the critical vulnerability but a severity score of 9.8 has been added to the report.
As per Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 cybersecurity team, njRAT is being used to download and execute secondary-stage payloads from Pastebin, scrapping the need to establish a traditional command-and-control (C2) server altogether.
Key lawmakers in the House and Senate celebrated the inclusion of cybersecurity provisions they shepherded into the final annual National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA).
Proof-of-concept exploit code has been published this week for a new attack technique that can bypass the Kerberos authentication protocol in Windows environments and let intruders access sensitive network-connected services.
The server-client communication in certain versions of the WinZip file compression tool is insecure and could be modified to serve malware or fraudulent content to users.
The OpenSSF announced at the Black Hat Europe conference the availability of an open-source tool designed for evaluating the ability of static analysis security testing (SAST) products to detect vulnerabilities.
A new card skimmer has been found using an innovative technique to inject highly convincing PayPal iframes and hijack the checkout process on compromised online stores.
Kaspersky’s security researchers stumbled across a new PowerShell backdoor by the DeathStalker group that has several anti-detection tactics from mouse movements detection to MAC addresses filtering.
Google patched ten critical bugs as part of its December updates. The worst of the bugs was tied to the Android media framework component and gives attackers remote control of vulnerable devices.