To carry out the scam, the scammer needed more details on equipment used at an unnamed oil company to make malicious emails to the company’s employees more believable, researchers wrote.
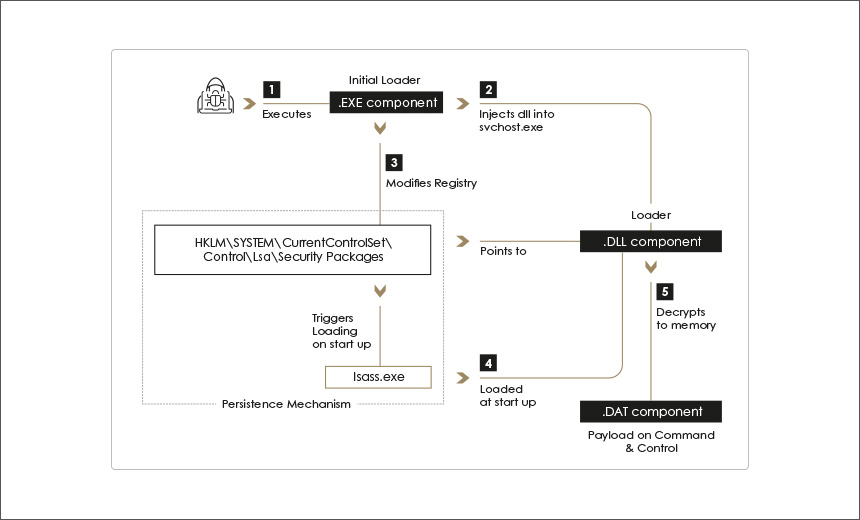
Changes injected into a software build pipeline or continuous integration (CI) process will be included in the signed final product, altogether defeating the purpose of the signature.
The flaw was classified by Microsoft as wormable, indicating that malware exploiting it might be able to spread automatically between vulnerable machines on the network with no user interaction.
Cybersecurity researchers point out that threat actors can use personal information gleaned from images to craft targeted scams, putting personal and corporate data at risk.
It can be unarguably stated that North Korea and cybercrime go hand in hand. The nation is highly focused on reinforcing its cyber capabilities, by all means necessary, and creating more than just a nuisance.
A user on a popular hacking forum was purportedly selling the stolen credentials from 6 South American countries for the Swiss-based Adecco Group, the second-largest staffing provider in the world.
The healthcare industry remains most at risk, particularly through web gateways, and phishing is still a high-risk vector in this sector, according to cybersecurity experts.
The Lazarus Group, a North Korean hacking operation also known as Hidden Cobra, is deploying TFlower ransomware, using its MATA malware framework, security firm Sygnia reports.
Flaws like these in boot loaders allow circumvention of UEFI Secure Boot, a verification mechanism for ensuring that code executed by a computer’s UEFI firmware is trusted and not malicious.
The proliferation of offensive cyber capabilities (OCC) presents an expanding set of risks to states and challenges commitments to protect openness, security, and stability in cyberspace.