Historically, organizations have taken a siloed approach to defending against cyber threats. A new threat pops up, and the IT security team invests in and purchases a new point solution to address it.
The attacks increased as academic institutions shifted to remote learning and teaching, leaving their networks vulnerable to threat actors.
CrowdStrike revealed that there has been a humongous increase in interactive intrusion activity. There has been a fourfold increase in these activities in the last two years.
The free service is being provided by the GCHQ-backed National Cyber Security Center to the UK’s smallest businesses who, like most others, have been working remotely during the pandemic.
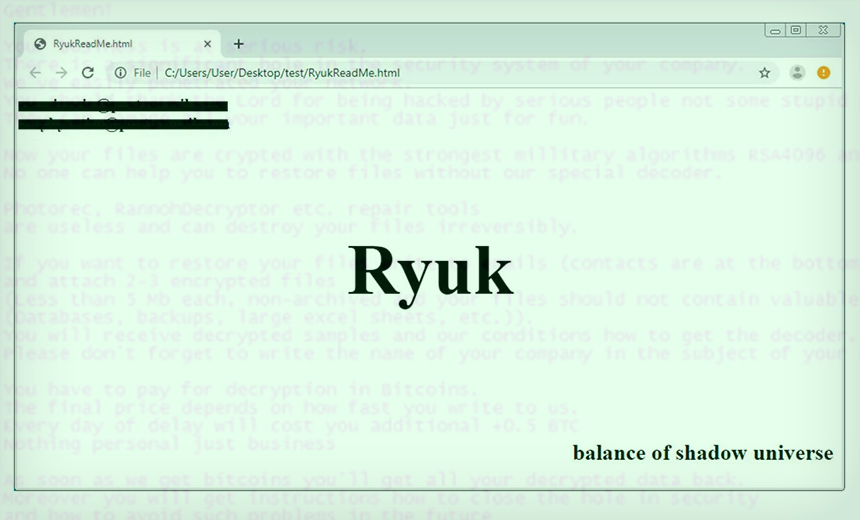
The developers behind the notorious strain of crypto-locking malware have given their attack code the ability to spread itself between systems inside an infected network.
The unverified email screenshots appear to relate to Bahamas-based Deltec, which has a banking relationship with Tether, and a discussion over asset backing. Tether says the documents are “bogus.”
Dubbed “Gootloader,” the expanded Javascript-based malware delivery system comes amid a surge in the number of infections targeting users in France, Germany, South Korea, and the U.S.
Fraudsters from countries like China, Nigeria, and Russia buy stolen personal information online from previous identity thefts and then use it to make bogus claims on state unemployment systems.
“COVIDGuardian”, the first automated security and privacy assessment tool, tests contact tracing apps for potential threats such as malware, embedded trackers, and private information leakage.
An AOL email phishing campaign is underway to steal users’ login name and password by warning recipients that their account is about to be closed if they do not login and verify it within 72 hours.