The leaked data poses serious risks, as threat actors could potentially disrupt services, launch phishing campaigns, and engage in “doxxing” and “swatting” activities, putting customers at risk.
EDF, the company operating nuclear power plants in the UK, is facing increased regulatory attention after an inspection of its cybersecurity practices. The company failed to provide a comprehensive cybersecurity improvement plan.
The attackers made use of legitimate tools like Plink to configure port-forwarding rules, enabling remote access via the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and modified Windows firewall rules to facilitate their activities.
To mitigate the risk, organizations should implement strategies such as employee training, geolocation and geofencing, endpoint data encryption, and secure storage solutions.
A hacker has leaked 4.1 million stolen genetic data profiles from 23andMe, a DNA testing company, on a hacking forum. This follows a recent leak of 1 million profiles of Ashkenazi Jews.
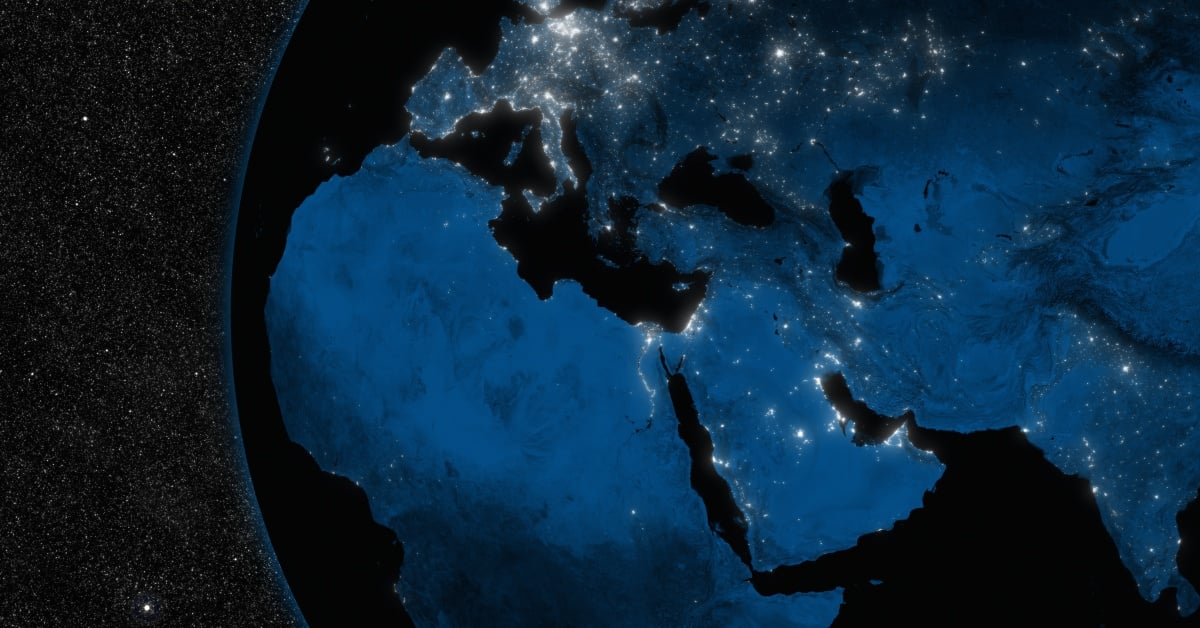
A hypothetical cyberattack on a major financial services payment system could result in global economic losses of up to $3.5 trillion over a five-year period. The United States, China, and Japan are the countries most at risk.
The attackers employed sophisticated techniques, including exploiting a vulnerability in Internet Explorer and using specialized malware modules for data exfiltration, highlighting the increasing complexity of targeted attacks.
The marketplace, which used an online payment system called Perfect Money, offered illicit cryptocurrency exchange services and listed credentials belonging to 350,000 devices for sale globally.
A critical security flaw in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances (CVE-2023-4966) is being actively exploited, potentially allowing hijacking of authenticated sessions and bypassing multi-factor authentication.
Oracle has released 387 new security patches to address vulnerabilities in its own code and third-party components, with over 40 patches addressing critical severity flaws.