A new federal strategy to make manufacturers liable for insecure software requires an attainable safe harbor policy and could be a disincentive for them in sharing important vulnerability info with the government, according to industry observers.
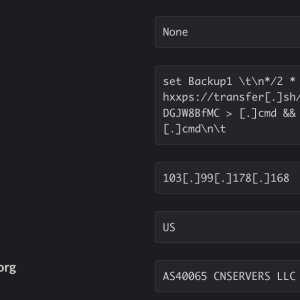
Cado Labs researchers recently discovered a new cryptojacking campaign targeting insecure deployments of Redis database servers. Threat actors behind this campaign used the free and open source command line file transfer service transfer.sh.
A leader of an international crime network that attempted to launder more than $25 million in fraudulently obtained funds, including through business email compromise, received a sentence of more than a decade in prison.
An analysis conducted by researcher Anurag Sen at CloudDefense.AI showed that the exposed Falkensteiner customer data was associated with Gustaffo, a company offering IT solutions for the hospitality industry.
The breach exposed reams of sensitive personal data for more than 550,000 users, including customers’ full names, home addresses, email addresses, plaintext passwords, and telephone numbers.
Individuals confirmed to be impacted by the incident will be notified directly. WH Smith says that special measures to support them will be put in place. This presumably will include identity protection services.
The new strategy has five pillars: Defend critical infrastructure; Target and disrupt threat actors; Use market forces to improve security and resilience; Invest in resilience; and Enhance international partnerships.
Vulnerabilities associated with Microsoft Exchange Server and some virtual private networks, many of which were first disclosed in 2017, continue to be a popular route for hackers to exploit, a report from exposure management company Tenable found.
American fast food chain Chick-fil-A has confirmed that customers’ accounts were breached in a months-long credential stuffing attack, allowing threat actors to use stored rewards balances and access personal information.
A new report by Kaspersky states that almost 200,000 new mobile banking trojans surfaced in 2022, marking a 100% increase from 2021, with China being the most affected, followed by Syria and Iran. RiskTool-type potentially unwanted software accounted for the most distributions at 27.39%, followed by adware at 24.05% and trojan-type malware at 15.56%.